阅读:0
听报道
推文人 | 闫雪凌
原文信息:Cheng, Hong, Ruixue Jia, Dandan Li, and Hongbin Li. 2019. "The Rise of Robots in China." Journal of Economic Perspectives, 33 (2): 71-88.
一、背景
关于工业机器人对经济影响的研究,国外各路大神都已有诸多研究,如Acemoglu and Restrepo、Graetz and Michaels的系列文章,纯理论模型和实证文章都已有多篇,人美心善的闫老师的AI助手已在香樟公众号上推过至少三篇。作为世界上最大的发展中国家,中国的工业机器人使用情况如何?对经济发展又有怎样的影响?目前的研究还不多,需要特别安排一下。
二、内容
文章内容主要分两个部分:第一部分主要是直观介绍中国工业机器人发展现状,包括横向纵向比较、国家政策支持等,第二部分是使用微观企业数据实证研究使用工业机器人对企业的影响。
(一)中国工业机器人发展现状
1、使用情况:
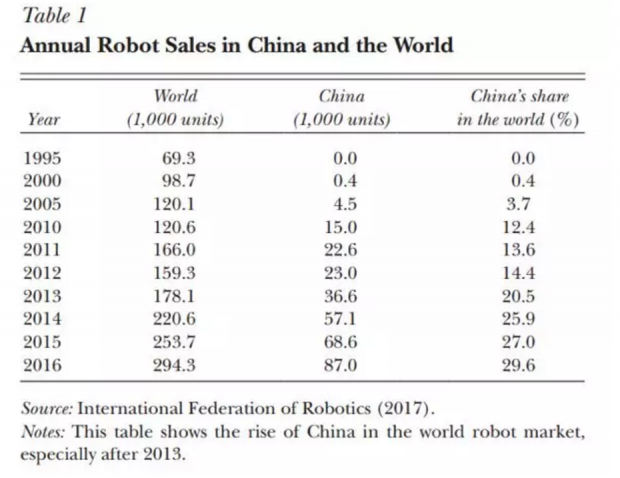
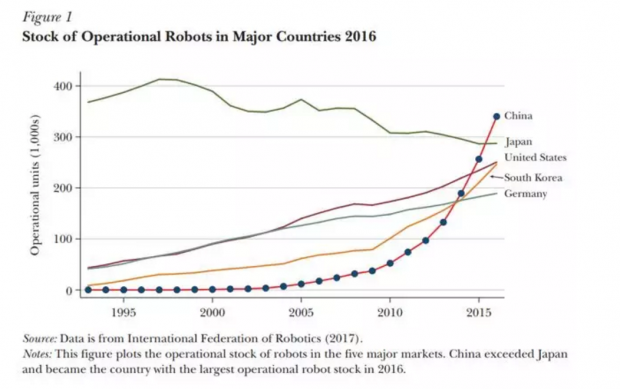
从使用数量来看,无论是与世界相比,还是与全球使用工业机器人的几个大国美国、日本、韩国、德国相比,中国的工业机器人使用都呈现起步晚、发展快、份额多这三个特点。
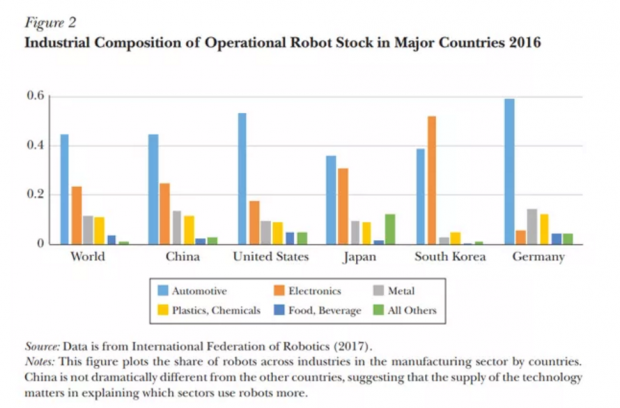
从应用行业上来看,中国工业机器人使用最多的行业是汽车行业,这与世界其他国家的情况一致,其次是电子行业。作者进一步构建了中国机器人使用的行业Herfindahl–Hirschman index,发现行业集中度有所下降,这说明工业机器人应用到了各行各业中。
2、生产情况
中国制造的工业机器人的发展随着使用的增长有着更快速的提升,从直观的数字上来看,2012年,中国制造的机器人只有5800台,而到2017年,短短五年间,这个数字翻了20倍,达到13万台之多,而其中29%是中国本土企业所生产。
3、政府政策支持
近年来中国劳动力市场的压力一直很大,面临着“人口红利”逐渐消失、老龄化加剧、劳动力成本增加等诸多现实问题。基于此,中国政府大力出台政策措施,鼓励中国工业机器人的使用和制造,推动中国经济的转型升级发展。具体来说,有以下三个比较重要的政策:
① 2013年,工业和信息化部关于推进工业机器人产业发展的指导意见
② 2015年,《中国制造2025纲要》
③ 2016年,三部委联合印发机器人产业发展规划(2016-2020年)
4、社会态度
对于机器人的大量投入使用,最为关心的一个问题还是,其对中国的经济发展到底有着何种影响。在这一部分,作者给出了一些直观的证据,表明从整体上看,其对中国经济的影响是正面的,大众担心的劳动替代效应,从政府的角度来讲,很少提及,多数官方报道都侧重于强调其对经济的促进作用;从媒体报道的角度来讲,作者搜集了2009-2019年人民日报发表的346篇中央政府对于工业机器人的报道,其中提到“技术”、“革新”等关键词的有206篇,而提及“劳动替代”的为85篇。由上可见,作者认为当前政府对于工业机器人的发展持较为乐观的支持态度。
(二)结合中国企业-劳动力匹配调查(CEES)的实证研究
1、数据:CEES2016年数据
CEES是武汉大学联合斯坦福大学、香港科技大学和中国社科院开展的“中国企业-劳动力匹配调查”,在2015、2016、2018三年分别开展了三次,并实现了对样本的追踪。
本文使用的2016年数据,是在广东省和湖北省所调查,包括了两个省的26个县共有1115家有效企业样本,覆盖了8848位劳动者,其中3691位是生产线上的工人。
(补充一句,目前CEES数据已经到2018年,有了更全面的拓展,详细情况请参考文末另一篇中文文献。)
2、 问题:CEES2016中关于企业使用机器人有三个问题
① 2015年企业在生产过程中是否使用了工业机器人
② 工业机器人购买价格是多少?
③ 政府是否对企业购买工业机器人有补贴
3、 实证策略
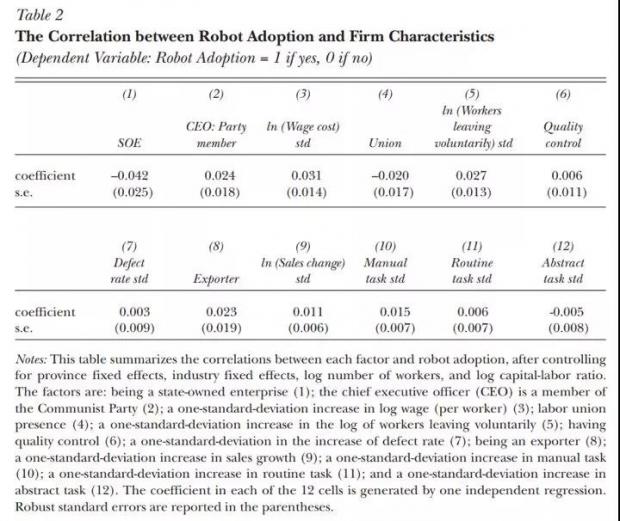
结合企业的特性以及政府的政策,实证研究当前在中国,什么样特点的企业更倾向使用工业机器人,并探讨了政府支持、劳动力压力、市场因素等多方原因对于企业是否使用工业机器人的影响。
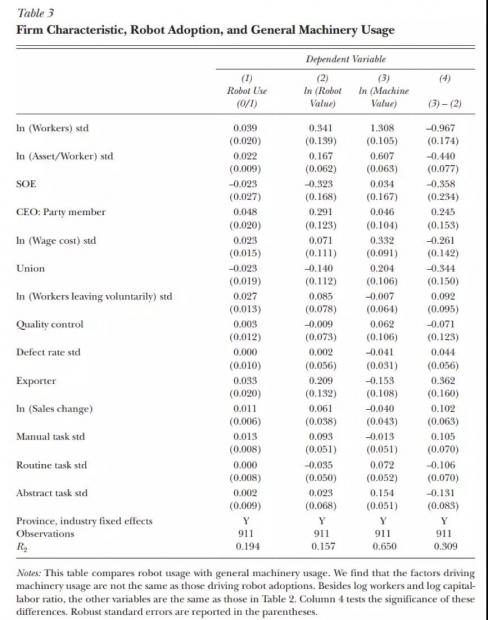
三、结论
1、无论从使用还是制造,中国工业机器人都在迅速崛起。
2、当前中中央政府的政策和各地不同补贴措施都会进一步促进中国工业机器人的发展。
3、短期来看,大量工业机器人的使用会对现有传统里有一定压力,但在中国人口红利逐步消失、老龄化加剧、用工成本增加等多种背景交叉影响看,工业机器人对中国经济的长期发展有巨大的促进作用。
四、写在最后
这是人美心善的闫老师的AI助手推送的有关工业机器人使用对于经济影响的第四篇论文,在这篇论文以中国为研究对象,让我们进一步直观了解中国工业机器人使用大大致情况。
另外,程虹老师还有一篇这一话题的中文文献可以供各位作者参考阅读:《机器人在中国:现状、未来与影响——来自中国企业-劳动力匹配调查(CEES)的经验证据》,程虹等,2018,《宏观经济研究》。
期待更多有关人工智能、机器人等投产使用对经济影响的文章出现,毕竟我们无法抵挡科技的进步,不如以一种更开放包容的心态与它一同成长。
Abstract
The Rise of Robots in China(没有Abstract,所以放上Conclusion)
In this paper, we have sought to describe some key patterns in the rise of robots in China. At the aggregate level, the rise of robots has accompanied a decline in the growth of the working-age population and an increase in wages, suggesting that the rising cost of labor is one underlying driver of robot usage in China. Because China is a global leader in the production and consumption of automotive and electronics, the two leading industries in robot adoption, China probably will play an even more important role in the robot market in the future. The Chinese government’s industrial policies are also likely to affect both robot adoption and production.
Using the China Employer-Employee Survey (CEES) data, we further provide firm-level evidence of the rise of robots in Chinese manufacturing firms. We believe that the evidence we have found on the roles of government and the market in driving the adoption of robot technology is particularly important. These analyses are some initial steps towards understanding the causes and consequences of the increasing use of robots in Chinese manufacturing. Such consequences include effects on firm productivity, complementarity/substitution between humans and robots, and other labor market outcomes.
At this stage, the threat of job replacement is not a high-priority concern in the mind of China’s government or its citizens. Government policies are motivated by the challenges of labor costs and labor shortage, as well as the imperative to lead a new wave of Industrial Revolution. For employers, the labor force challenges are indeed important considerations for robot adoption, as shown by our analysis. For employees, the high voluntary turnover rates and the lack of strong and independent unions may partly contribute to their tolerance of robot adoption. It is conceivable, however, that the short-run consequences are different from those in the long run. We hope to make further progress on these questions by continuing to follow China’s manufacturing firms.

话题:
0
推荐
财新博客版权声明:财新博客所发布文章及图片之版权属博主本人及/或相关权利人所有,未经博主及/或相关权利人单独授权,任何网站、平面媒体不得予以转载。财新网对相关媒体的网站信息内容转载授权并不包括财新博客的文章及图片。博客文章均为作者个人观点,不代表财新网的立场和观点。



 京公网安备 11010502034662号
京公网安备 11010502034662号 